National Early Warning Score
Parameters
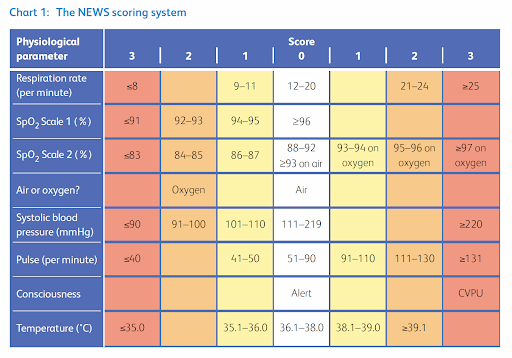

- respiration rate
- oxygen saturation
- systolic blood pressure
- pulse rate
- level of consciousness or new confusion*
- temperature.
- inspired oxygen
What NEWS does?
• It provides a baseline measure of an individual’s
physiological functioning (from a gathered sequence
of vital signs recordings);
• It measures the effectiveness of some treatment
interventions when there is a change in NEWS;
• It provides a risk assessment of an individual based
on recorded observations;
• It can assist in timely escalation of clinical response
in the event of an acute physiological deterioration
when there is an increase in NEWS.

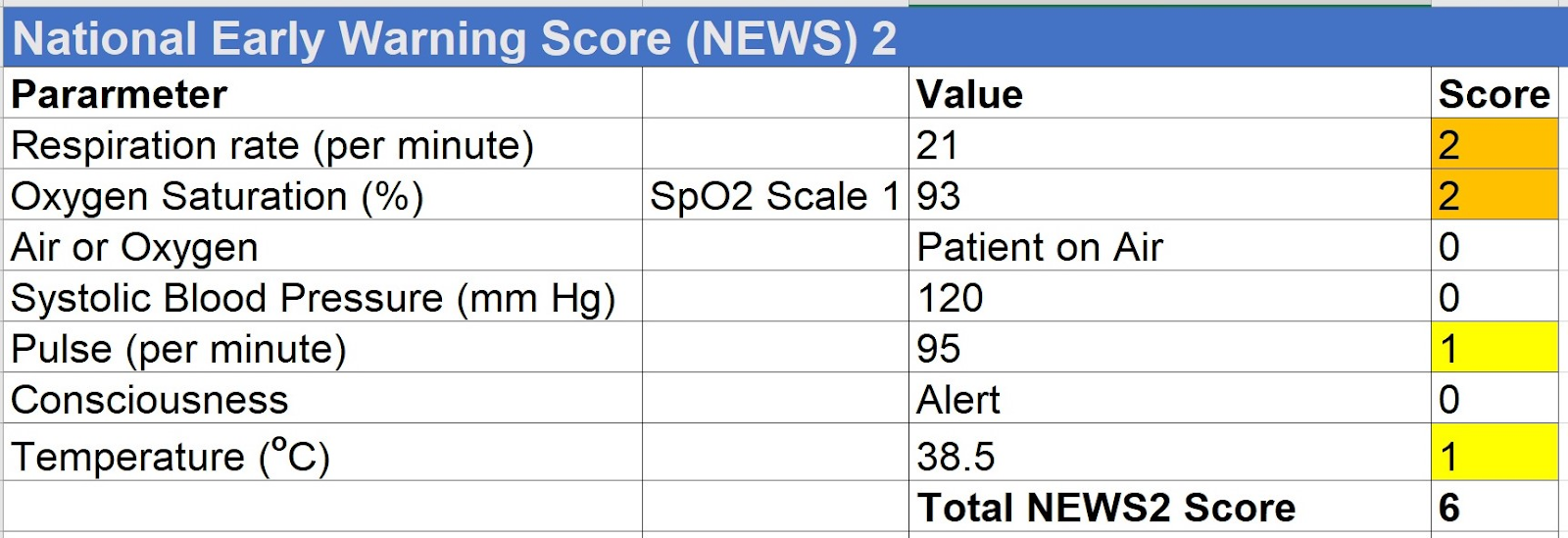
Example Scenario
Mr Smith is 52 year old gentleman who attends the emergency department with fever, cough and pleuritic pain with following vitals:
- Respiratory rate: 21/min
- Oxygen saturation : 93%
- On air
- Systolic blood pressure: 120 mmHg
- Heart rate : 95/min
- Consciousness: Alert
- Temperature: 38.5 °C


What is SBAR?
SBAR is a tool for communication and stands for:
• Situation. Patient/ client’s details, identify reason
for this communication, describe your concern.
• Background. Relating to the patient/ client/
service user/ resident significant history; this may
include medications, investigations, treatments
.
• Assessment. What is your assessment of the
patient/ client or situation. This can include clinical
impressions/ concerns, vital signs if relevant.
• Recommendation. Be specific, explain what
you need, make recommendations, clarify
expectations and confirm actions to be taken.
Mnemónica ISBAR: auxiliar de memória que permite através de formas simples, memorizar construções complexas, para serem utilizadas na transmissão verbal, em que
I: corresponde à Identificação,
S: à Situação atual,
B: aos Antecedentes,
A: à Avaliação,
R: às Recomendações. Identificação: Identificação e localização precisa dos intervenientes na comunicação (emissor e recetor) bem como do doente a que diz respeito a comunicação; Situação atual: Descrição do motivo atual de necessidade de cuidados de saúde; Antecedentes: Descrição de factos clínicos, de enfermagem e outros relevantes, diretivas antecipadas de vontade; Avaliação: Informações sobre o estado do doente, terapêutica medicamentosa e nãomedicamentosa instituída, estratégias de tratamento, alterações de estado de saúde significativas; Recomend
https://www.dgs.pt/directrizes-da-dgs/normas-e-circulares-normativas/norma-n-0012017-de-08022017-pdf.aspx
Mnemónica ISBAR: auxiliar de memória que permite através de formas simples, memorizar construções complexas, para serem utilizadas na transmissão verbal, em que
I: corresponde à Identificação,
S: à Situação atual,
B: aos Antecedentes,
A: à Avaliação,
R: às Recomendações. Identificação: Identificação e localização precisa dos intervenientes na comunicação (emissor e recetor) bem como do doente a que diz respeito a comunicação; Situação atual: Descrição do motivo atual de necessidade de cuidados de saúde; Antecedentes: Descrição de factos clínicos, de enfermagem e outros relevantes, diretivas antecipadas de vontade; Avaliação: Informações sobre o estado do doente, terapêutica medicamentosa e nãomedicamentosa instituída, estratégias de tratamento, alterações de estado de saúde significativas; Recomend
https://www.dgs.pt/directrizes-da-dgs/normas-e-circulares-normativas/norma-n-0012017-de-08022017-pdf.aspx
Benefits of NEWS
1. Improved patient safety by accurate recording
and auditing of vital signs measurements
2. Saving of training time where staff work in many
different organisations: (essentially) one system
to be learned than a previous large variety of
different EWS systems
3. NEWS becomes part of the language used in
communication between different health care
professionals about patients
4. Formalisation and clarity of escalation responses
for patients who deteriorate in physiological
condition.
5. Surveillance of baseline physiology to detect
departure from normal physiology; collection of
trend information allows monitoring of variance
to assure appropriate changes in care where
required.
6. Compliance with national recommendations
for acute illness management; national
recommendations tend to be based on better
evidence than can be obtained locally.
SHOUT
S Sepsis
H Hypovolaemia
O Obstruction
U Urine Analysis
T Toxins
SNOOP
S SEPSIS
N NEWS
O OXYGENATION
O OUTPUT OF URINE
P PAIN
i have nice artical read How To Reduce Belly fat.
ResponderEliminarReduce Belly fat