Common Lung Diseases — Overview and Investigations by lecturio
Table of Contents
Range of lung diseases
The Big 4 Lung Diseases
- COPD — most common cause of acute medical admissions
- Asthma — most common chronic respiratory disease
- Lung cancer — most common fatal cancer in the Western world for both men and women
- Pneumonia — most common serious infectious disease
Other common respiratory diseases
- Infectious: tuberculosis, empyema
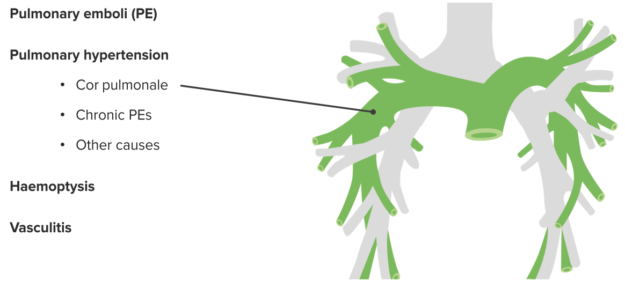
- Pulmonary emboli
- Bronchiectasis
- Interstitial lung disease and sarcoidosis
- Pleural effusions and pneumothorax
- Obstructive sleep apnea
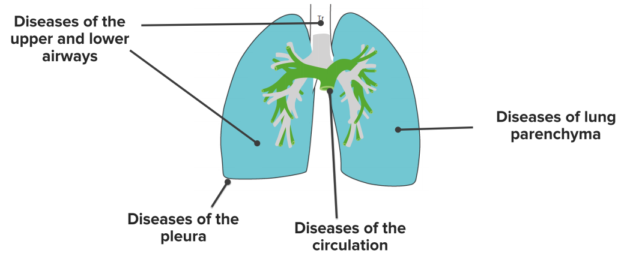
Range of Lung Diseases
Diseases of the airways
Lung parenchyma (alveoli and interstitium)
Circulation
Pleural diseases
Other
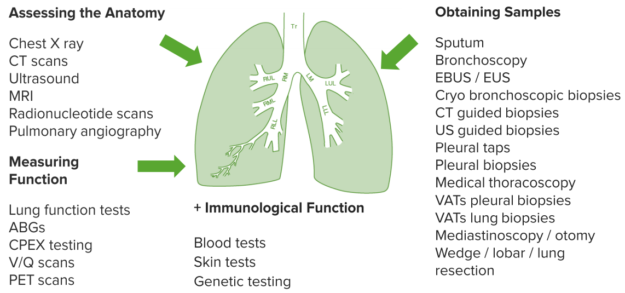
Investigation of Lung Disease
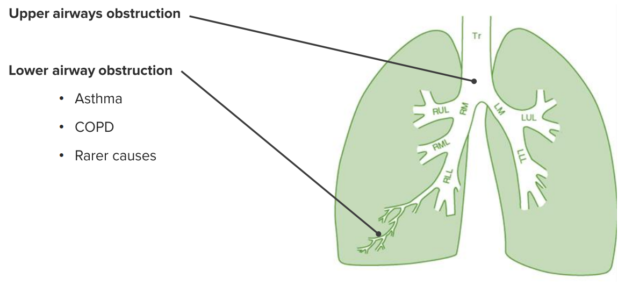
Different Causes of Large Airway Obstruction
Acute upper airway obstruction
Chronic upper airway obstruction
Large Airway Obstructions: Clues
-
Minimal variability in peak flow/ spirometry
- Positional symptoms rather than diurnal
- Inspiratory wheeze (Stridor)
- Past history of intubation/ tracheal disease
- Characteristic flow volume loop
- Fall in PEFR relatively greater than fall in FEV1
Bronchoscopy
- Visual confirmation
- Biopsies to confirm the cause (but can bleed…)
- Treatment as well
Treatment of acute presentation
- Sit the patient up
- High flow oxygen or heliox (mixture of oxygen and helium) via mask
- Intravenous high-dose corticosteroids (reduce edema around obstruction)
- Nebulized salbutamol and adrenaline
- Intravenous fluid replacement
- Potentially urgent intubation or tracheostomy or bronchoscopy intervention
Treatment of chronic obstruction
Chronic—relieve the obstruction by
- Treat underlying cause if possible
- Bronchoscopic interventions e.g.
- Stents
- Laser ablation
- Surgical interventions
- Remove cause
- Tracheostomy

Comentários
Enviar um comentário