Congenital Heart Defect (CHD) — Lesions
Image: “Illustration demonstrating a narrowing of the large blood vessel (aorta) that leads from the heart.” by BruceBlaus – Own work. License: CC BY-SA 4.0
Definition and Epidemiology of Congenital Heart Defects
Congenital heart diseases are structural heart defects present since birth with clinical manifestations seen in the prenatal period through adulthood. Obstructive lesions include conditions with increased ventricular outflow obstruction on either side of the heart.
While congenital heart diseases account for the most common birth defects affecting about 1% of the babies born, of these, ventricular septal defects are the most common heart defects.
- Congenital aortic stenosis is known to occur in about 3 to 5 per 1,000 live births, affecting males more than females.
- Congenital bicuspid aortic valve has been known to be the most common cause of aortic stenosis in patients older than 70 years of age.
- Coarctation of aorta accounts for 6 – 8% of birth defects and affects males twice as much as females. 10 – 20% of patients with Turner’s syndrome will be affected by this heart defect as well. 40 – 80% of patients with coarctation of aorta are associated with the bicuspid aortic valve.
Classification of Obstructive Lesions in CHD
Obstruction to inflow
- Cor triatriatum
- Obstructive lesions of mitral valve
Obstruction to right ventricle
- Pulmonary valve stenosis
- Infundibular stenosis
- Branch pulmonary artery stenosis
Obstruction to left ventricle
- Aortic stenosis
- Coarctation of aorta
Miscellaneous
- Coronary artery abnormalities
- Congenital mitral and tricuspid valve regurgitation
Pathophysiology of Obstructive Lesions in CHD
Conditions with increased left ventricular outflow obstruction
A valvular obstruction is overcome by increasing the systolic pressure of the left ventricle, brought about by concentric hypertrophy of the ventricle. The muscular ventricle empties completely, but takes longer than the normal systolic time. This is fundamental to the signs perceived during the cardiovascular examination.
- Prolonged left ventricular ejection time causes a delayed closure of the aortic valve; hence, delayed A2.
- Flow across aortic obstruction during systole associated with aortic ejection systolic murmur.
- Murmur is palpable as a thrill AT second RICS, suprasternal notch and carotid vessels.
- Prolonged ejection produces a characteristic low amplitude pulse – slow rise to a sustained peak followed by a downslope.
With increasing severity of aortic stenosis, marked left ventricular hypertrophy occurs resulting in reduced distensibility. The left ventricular diastolic pressure rises, secondary to which left atrial pressure also rises to fill the ventricle during diastole. The effect on heart sounds are:
- Palpable and audible fourth heart sound owing to forceful left atrial contraction.
- With sustained obstruction, left ventricular failure ensues giving rise to a third heart sound.
Pathologically, the obstruction maybe present:
- At the level of the valve (valvar): This results from either a unicuspid or bicuspid aortic valve.
- Above the valve (supravalvar): This results from an obstruction in the root of the aorta above the aortic valve as in Williams syndrome.
- Below the valve (subvalvar): This may be discrete or membranous, fibromuscular or muscular (hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy).
Conditions with increased right ventricular outflow obstruction
The obstruction to the flow across the narrow pulmonary valve is overcome by an increased right ventricular systolic pressure and concentric hypertrophy. The right ventricular systolic ejection duration is prolonged, but the distensibility is reduced. The right atrial pressure consequently increases to fill the right ventricle during diastole. Clinically, these pathophysiological mechanisms manifest as murmurs and additional heart sounds.
- Delayed P2 owing to prolonged right ventricular systolic ejection duration.
- Delayed P2 results in a wide and variably split second heart sound.
- The flow across the obstructed pulmonary valve is associated with a diamond shaped ejection systolic murmur. The severity of the obstruction can be determined by the relation of the murmurs with inspiration and expiration.
- A forceful right atrial contraction results in an audible right fourth heart sound, while it is the right ventricular failure responsible for the third heart sound.
Coarctation of aorta
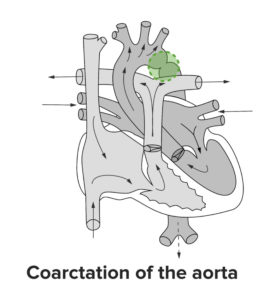
A sharp indentation at the junction of the arch with descending aorta involving all the walls except the medial one is characteristic of coarctation of the aorta.
In fetal circulation, much of the blood flow in the descending aorta comes from the right ventricle by way of a wide ductus arteriousus. The left ventricular blood volume forms a much smaller fraction of the content of the descending aorta as much of it empties into the innominate, left carotid and left subclavian arteries.
At birth, the isthmus (segment of the aorta distal to the left subclavian artery but proximal to where the ductus arteriosus joins the aorta) is the narrowest part of the aorta. When the ductus arteriosus closes, the descending aorta receives all of its blood supply from the left ventricle via ascending aorta; therefore, neonates with a severe coarctation become symptomatic owing to primarily two physiological mechanisms:
- Pressure overload proximal to the coarctation: This leads to left ventricular hypertrophy and hypertension in the upper parts of the body. While the exact mechanism for the cause of hypertension is not known, aortic obstruction is considered at least partially responsible for it.
- Hypoperfusion distal to the coarctation: Malperfusion of abdominal organs and lower extremities increase the risk of sepsis. However, the pressure gradient ultimately increases the collateral circulation to these areas via intercostal, internal mammary and other arteries. The narrow pulse pressure in the descending aorta distal to the coarctation has been implicated as the cause behind renal mediated increase in blood pressure. The collateral vessels that develop tend to decompress the hypertensive segment that results in two cardiovascular features:
- Collaterals enlarge and become palpable at lower borders of the ribs often late in childhood or adolescence.
- The resting blood pressure in the upper extremities may become normal, to rise only on exercise.
Clinical Features of Obstructive Lesions in CHD
Aortic stenosis
Symptoms
- Mild to moderate stenosis: usually asymptomatic.
- Severe stenosis: Initial symptom is exertional dyspnea or syncope or angina on the effort. The presence of any of these three suggests severe AS, however, a lack of these does not rule out its possibility.
Signs
- Mild to moderate stenosis:
- Normal BP
- Wide pulse pressure
- Heaving apical impulse
- Normal S1
- Normal split S2 in mild stenosis
- Closely split S2 in moderate stenosis
- Ejection systolic murmur heard during inspiration in mild stenosis and during both inspiration and expiration in moderate stenosis
- Severe AS:
- Narrow pulse pressure
- Normal S1
- Paradoxically split S2
- S3 and S4 present
- According to obstruction site:
- Valvar:
- S1 followed by aortic ejection click
- The click precedes the murmur
- It is heard at the apex
- Subvalvar:
- Ejection click is absent
- Supravalvar:
- Williams syndrome is associated with elfin facies, mental retardation and dental abnormalities.
- Loud A2 due to high pressure proximal to obstruction.
- Higher systolic BP in right arm > left arm as jet of blood through narrowing may be directed to innominate artery.
Pulmonic stenosis
Symptoms
- Mild to moderate stenosis: usually asymptomatic
- Severe stenosis:
- Exertional dyspnea present
- Palpitation, easy fatigability, chest pain
Signs
- Mild to moderate stenosis: usually no significant signs seen except ejection systolic murmurheard during inspiration in mild stenosis and during both inspiration and expiration in moderate stenosis.
- Severe stenosis:
- Left parasternal heave due to enlarged RV
- Normal S1
- Widely split S2 with delayed P2
- S3 and S4 present if RV failure ensues
- Ejection systolic murmur heard during expiration
Coarctation of aorta
Symptoms
- When less severe, during infancy it may be asymptomatic or present with subtle symptoms of intermittent claudication, pain and weakness of legs, dyspnea on running.
- When significant, infants fall ill as soon as the duct closes. Heart failure, renal insufficiency and metabolic acidosis develop in the first 7 – 10 days that often mimic a picture of sepsis.
Signs
- Strong pulses and hypertension in upper extremities in contrast to weak pulses and unobtainable BP in lower extremities.
- Prominent arterial pulsations in carotid vessels.
- Heaving apical impulse.
- Accentuated S1 with loud M1.
- Normally split S2 but with delayed and accentuated A2.
- Continuous late ejection systolic murmur heard.
Investigations for Obstructive Lesions in CHD
Usually, a relevant clinical history and proper physical examination provide sufficient clues to the diagnosis. In a few ambiguous cases, a chest X-ray, electrocardiogram and, on rare occasions, an echocardiogram help in clearing the air on suspects.
Chest X-ray
This investigation finds use primarily in pointing out a prominent vessel seen as an enlarged shadow or assessing the change in cardiac size.
Coarctation of aorta:
- A characteristic ‘3’ sign appearance of the coarctation in the upper left mediastinal shadow is seen. This can be confirmed on a barium swallow that shows a characteristic ‘E’ sign at the site of coarctation.
- Normal sized heart with the prominent ascending aorta and aortic knuckle.
- Characteristic notching of lower borders of ribs seen in children more than 10 years of age.
Aortic stenosis:
- Heart size may be normal but, when enlarged, it indicates severe AS with left ventricular failure.
- Calcification of cusps may be present.
- Post-stenotic dilatation of ascending aorta is seen in valvar and sub valvar aortic stenosis.
Pulmonic stenosis:
- Normal sized heart.
- Normal pulmonary vasculature in all grades of severity.
- Post stenotic dilatation in the main pulmonary artery.
ECG
While the axis deviation can hint towards a possible hypertrophy of the corresponding ventricle, some characteristic wave patterns are also seen.
Pulmonic stenosis:
- Right axis deviation and right ventricular hypertrophy.
- Pure ‘R’ complex in V1 leads suggests systolic overload of the right ventricle.
- P-pulmonale suggests severe PS.
Coarctation of aorta:
- Left ventricular hypertrophy
Aortic stenosis:
- Left ventricular hypertrophy
- While a normal ECG does not exclude the presence of severe AS, ST and T changes suggest severe stenosis.
Echocardiography
In all obstructive lesions, it is useful to determine the site of the obstruction and confirm the presence of ventricular hypertrophy. While in pulmonic stenosis, it can determine the severity of obstruction too; the pressure gradient across the aortic obstruction can be measured accurately using Doppler.
Treatment of Obstructive Lesions in CHD
Aortic stenosis
Conservative:
- Monitor regularly with 6 to 12 monthly ECG.
- Since severe AS is a risk for sudden death, patients are discouraged from outdoor games or strenuous physical activity.
Surgical:
- Balloon aortic valvuloplasty is the procedure of choice.
- Indicated when gradients are above 75mmHg.
- Avoided in supravalvar and subvalvar AS and in patients with significant aortic regurgitation.
- For these patients, aortic valve repair and replacement with the prosthetic valve may be considered.
Pulmonic stenosis
- Mild PS:
- Patients with gradients of 50mmHg or less are called for annual review
- Valvar PS:
- Balloon pulmonary valvuloplasty is the treatment of choice
- Infundibular PS:
- Surgical resection required
Coarctation of aorta
- Newborns and infants:
- Relief of coarctation to be done as soon as the diagnosis is made.
- Surgery is preferred.
- Recurrence rates of balloon dilatation are 90% and hence, undertaken only as interim palliation if heart failure and severe ventricular dysfunction are also present.
- Older children, adolescents and adults:
- Balloon dilatation performed.
Comentários
Enviar um comentário