Ectopic Pregnancy (Extrauterine Pregnancy) — Symptoms and Treatment
Eccyesis or tubal pregnancy refers to the implantation of the blastocyst outside the uterine cavity. Thereby, affected patients suffer from acute abdominal pain. Eccyesis or tubal pregnancy can be quickly diagnosed by means of an ultrasound and laboratory analysis. In severe cases, in the case of rupture and hemorrhage, the fastest possible action is required. Surgery should be considered as a therapeutical approach.
Table of Contents
Are you more of a visual learner? Check out our online video lectures and start your obstetrics and gynecology course now for free!
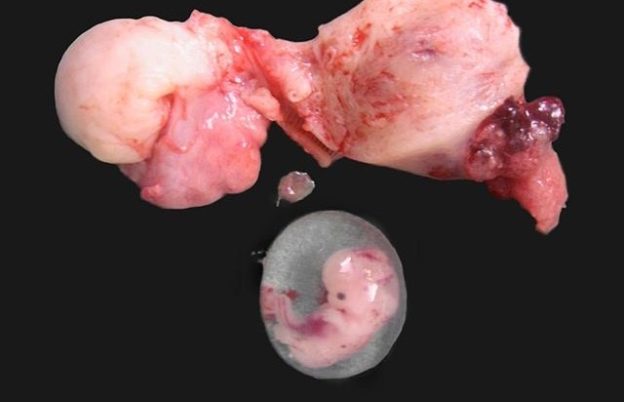
Image : “Ruptured cornual ectopic pregnancy” by Drvgaikwad, Dr. Vilas Gayakwad. License: CC BY-SA 3.0
Definition of Ectopic Pregnancy
Eccyesis or tubal pregnancy as ectopic pregnancy
In the case of ectopic pregnancy, the implantation of a blastocyst outside the uterine cavity (cavum uteri) takes place.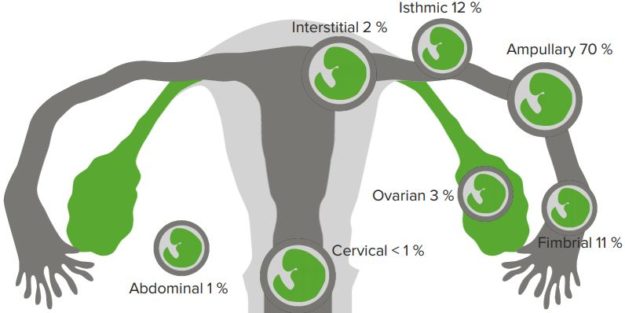
“Ectopic Pregnancy” Image created by Lecturio
Epidemiology of Ectopic Pregnancy
Cases of ectopic pregnancies have increased worldwide and have nearly doubled in the last ten years. This increase is attributed, among other things, to improved diagnosis. Secondly, intrauterine devices, ascending genital infections and infertility treatments also carry a high risk for ectopic pregnancy.Etiology of Ectopic Pregnancy
Causes of ectopic pregnancy
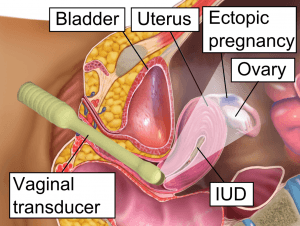
The most common location of for ectopic pregnancy is the fallopian tubes (= tubal pregnancy). The uterine tube is divided into such parts as: ampulla, isthmus and intramural. The ampulla portion is affected more often. The isthmic and intramural portions are affected less often.Approximately 1 % of ectopic pregnancies can affect the uterus, ovary, peritoneum (= abdominal pregnancy) or the cervix.
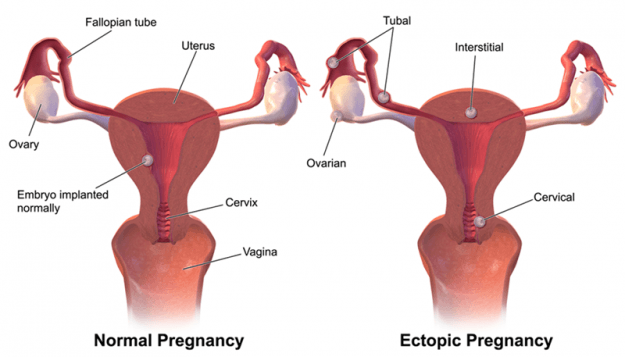
Image: “Ectopic Pregnancy” by BruceBlaus. Licence: CC BY-SA 4.0
Pathogenesis of Ectopic Pregnancy
Origin and development of ectopic pregnancy
The tubal mucosa is similar to the endometrium of the uterus in its ability to convert decidually, though not to a comparable extent. When a fertilized egg on the 5th or 6th day is not yet in the uterine cavity it settles at the corresponding location of nidation. This is usually the tube.The reasons may be disorders connected with the ovulation mechanism and tubal passage. The tube passage may be blocked by congenital anomalies or acquired obstacles. In addition, functional impairment is possible in terms of disruption of ciliar activity or tube motility.
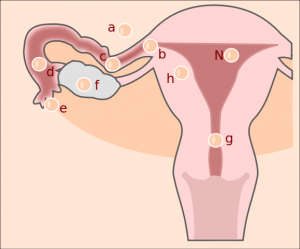
Image: “ectopic pregnancy” by Hic et nunc. Licence: CC BY-SA 3.0
Women with an intrauterine device (= IUD) are more often affected by ectopic pregnancy than women without IUDs. A decreased peristalsis might be the reason.
Clinic
Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy is an important differential diagnosis in cases of acute abdomen. Here, the symptoms vary greatly. It depends on the localization of the ectopic pregnancy, the condition of the product of conception (the embryo may be intact or already dead) and the age of the pregnancy. Thus, asymptomatic processes or very painful symptoms, up to circulatory shock, are possible. In addition, classical symptoms and signs of pregnancy may be present. These include breast tenderness and morning sickness.Initially, secondary amenorrhea is usually present. After about 5 weeks, unilateral pain appears in the adnexal region. This may also be accompanied by spotting. This bleeding usually corresponds to a hormonal withdrawal bleeding and less to the bleeding directly from the tube.
Pain symptoms in the shoulder area may arise, if the tube has been already ruptured (often the result of an ectopic pregnancy at the isthmus), and the case has already come to intra-abdominal bleeding. This is caused by an irritation of the phrenic nerve.
Diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
A clinical examination is indicated in addition to anamnestically described abdominal pain symptoms and secondary amenorrhea. Upon palpation of the lower abdomen, pain to pressure and pain on the movement of cervix are present. Subsequently, a laboratory analysis must be initiated. An increased serum beta-HCG concentration would be still detectable even with a negative pregnancy test. Thus, beta-HCG plays an important role in the diagnosis.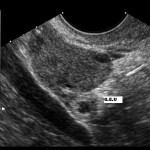
Image: “Ectopic pregnancy in ultrasound” by X.Compagnion. License: Public Domain
The diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy is suspected when all findings are compiled. However, the diagnosis must be confirmed by laparoscopy (or pelviscopy).
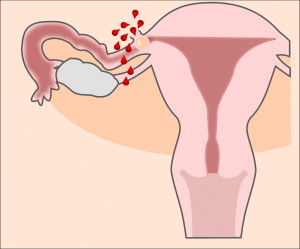
Image: “Schematic drawing of a rupture of the Fallopian tube in case of a ectopic pregnancy.” by Hic et nunc. License: CC BY-SA 3.0
Differential Diagnosis
Diseases similar to ectopic pregnancy
Other reasons for an acute abdomen must be ruled out, in addition to gynecological causes. These include the sigmoid diverticulitis or appendicitis.Other gynecological differential diagnoses include endometriosis, acute adnexitis, abortion, ovarian torsion and urological colic.
One must remember that none of the above differential diagnoses cause hemorrhagic shock and that any cause of hemorrhagic shock is a surgical emergency.
Therapy of Ectopic Pregnancy
Treatment of ectopic pregnancy
Therapeutically the diagnostic-therapeutic pelviscopy is used. Depending on the desire to have children the radical nature of the treatment may come into question. With an existing desire to have children a conservative organ-preserving procedure is applied. However, again this increases the risk of recurrence of an ectopic pregnancy.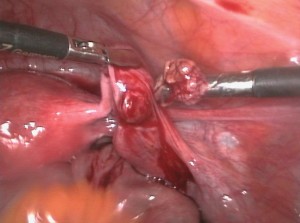
Image: “Removal of an ectopic pregnancy out of the right Fallopian tube” by Hic et nunc. License: CC BY-SA 3.0
In the early stages of ectopic pregnancy, a conservative action is also possible. It is characterized by drug therapy. In the case of a local treatment, prostaglandins or methotrexate can be injected. Likewise, a systemic drug therapy is possible with the intramuscular methotrexate administration. This medication causes death of the embryo. This conservative treatment is applied if there is no evidence of bleeding or rupture.
In the course of treatment, beta-HCG is regularly checked.
Prognosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
Recurrence probability of ectopic pregnancy
The recurrence probability is very high. It compounds 5 % – 20 % of all the affected.Review Questions
Correct answers can be found below the references.1. Which of the following diseases are not in the scope of the differential diagnosis of an ectopic pregnancy?
- Acute appendicitis
- Renal cyst on the right kidney
- Acute pelvic inflammatory disease
- Stone in the left kidney
- Imminent abortion
- Medical history
- Clinical examination of motor function of the lower extremities
- Beta-HCG determination in serum
- Ultrasound examination of the uterus and appendages on both the sides
- Abdominal palpation
- Tubes
- Cervix uteri
- Abdominal
- Vulva
- Vagina
Comentários
Enviar um comentário