Muscle Nerve Fiber Properties, Renshaw Cells and Muscle Reflexes
Table of Contents
Peripheral Nerve Fibers
A peripheral nerve consists of the following fibers:
- Sensory nerve fibers or afferent fibers
- Motor nerve fibers or efferent fibers
- Autonomic fibers
These, in turn, consist of the following parts:
- Axon
- Axolemma
- Myelin sheath
- Schwann cell
- Endoneurium
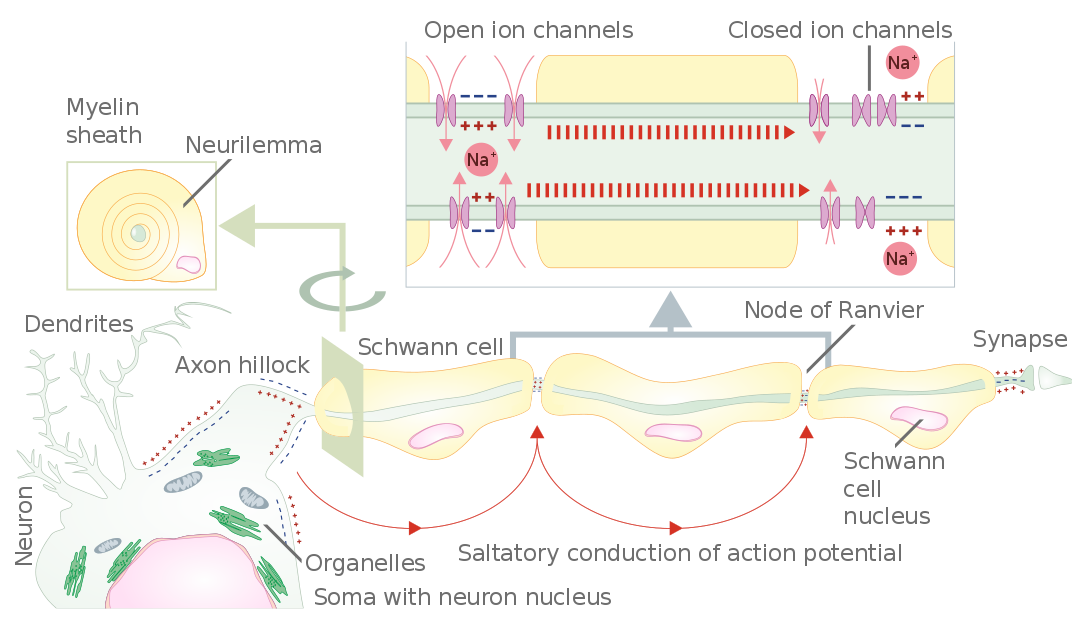
Image: “Schematic representation of the action potential propagation through myelinated nerve fiber of peripheral nervous system.” by Helixitta – Own work. License: CC BY-SA 4.0
Types of peripheral nerve fibers
The peripheral nerve fibers are divided into three groups: group A, B, and C.
Muscle nerve fibers
The muscle nerve fibers belong to the group A of peripheral nerve fibers.
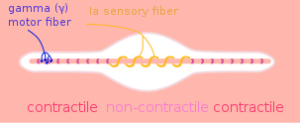
Muscle afferents
- Muscle spindles
- Golgi tendon organs
Muscle efferents
- Extrafusal
- Intrafusal
The sensory fibers of group A are sub-divided into:
Alpha fibers:
These have high conduction velocity of 80-120 m/s. Type Ia is large fibers innervating intrafusal fibers (see figure). They are related to muscle spindle primary endings and determine the velocity of muscle stretch. Type Ib fibers are related to golgi tendon organs. Their cell bodies are located in the dorsal root ganglia, adjacent to the spinal cord.
Beta fibers:
These are also referred to as type II fibers. They also carry sensory information related to muscle spindle activity. These fibers are non-adapting and have a conduction velocity of 35-75 m/s.
Delta fibers:
These are called type III fibers and carry the pain and cold temperature sensation.
Motor fibers
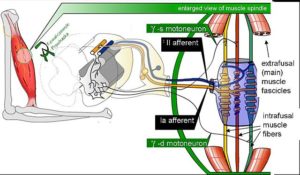
Image: “Muscle Spindle Model.” by Neuromechanics – Own Work. License: Public Domain
The motor fibers of group A are sub-divided into:
Alpha fibers:
These have myelinated, high conduction velocitytype of alpha motor neurons, which cause muscle contraction. These alpha motor neurons innervate the extrafusal fibers with a conduction velocity of 80-120 m/s.
Beta fibers:
These have myelinated beta motor neurons, which innervate the intrafusal fibers of the muscle spindles.
Gamma fibers:
These have gamma motor neurons with a conduction velocity of 15-30 m/s. They also innervate the intrafusal fibers of the muscle spindles.
Renshaw Cells
Renshaw cells are the inhibitory neurons, found in the gray matter of the spinal cord. They have two associations with the alpha motor neurons: They receive an excitatory collateral from the alpha neuron axon as they emerge from the motor root and thus are kept informed of how well the neuron is firing.
The cells also elicit an inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) in the alpha motor neurons and the gamma motor neurons. This inhibition is depressed through strong voluntary contractions and during dynamic contractions as compared to sustained contractions. These cells are, however, activated during weak voluntary contractions and during co-activation of the antagonists. The inhibitory effect of the Renshaw cell is due to the production of an inhibitory neurotransmitter glycine.
Clostridium tetani is a tetanus-causing gram-positive microorganism which targets the Renshaw cells and inhibits the release of glycine. The alpha and the gamma motor neurons’ activity go unchecked, which results in sustained contraction of the muscles eventually causing death.
Cutaneous Sensory Afferents
Classification of sensory afferent nerve fibers
Muscle Reflexes
A myotatic reflex, also known as the stretch reflex, is the contraction of muscle produced because of muscle stretching. When a muscle spindle is stretched, its neuronal activity increases. The alpha motor neurons are activated causing contraction of the stretched muscle, while the second set of neurons relaxes the opposing muscles. The gamma motor neurons regulate the sensitivity of the stretch reflex.
Examples
If a person standing straight leans on one side, the muscles lying close to the vertebral column will stretch. This will activate the motor neurons to cause contraction of these muscles and correction of the posture.
Jaw jerk reflex or the masseter reflex is done to see the patient’s trigeminal nerve. The mouth is slightly held open while the jaw is tapped. The contraction of masseter muscle will cause a slight closing of the mouth in normal individuals. This response is, however, well pronounced in upper motor neuron lesions.
The bicep reflex is done to test the C5-C6 spinal nerves. A tendon hammer is used to depress the biceps brachii tendon in the cubital fossa. This causes stretching of the bicep muscle. The reflex produces contraction of the bicep brachii muscle which is seen as the jerky movement of the forearm. A brisk reflex is seen in the upper motor neuron lesion, while a diminished response occurs in the lower motor neuron lesion.
The brachioradialis reflex (C6) is done by striking the brachioradialis tendon. The reflex is carried by the radial nerve. Slight extension at the wrist joint with supination and flexion at the elbow joint is seen.
The tricep reflex is done by tapping the tricep brachii tendon with a tendon hammer. Due to a sudden contraction of the tricep muscle, an extension of the elbow occurs. It tests the C7 and C8 cervical nerves. This reflex may be absent in sensory nerve disease, lower motor neuron disease, and myopathies. The irregular response is often noted in hyperthyroidism.
Patellar reflex or knee-jerk is performed to check the spinal segment L2-L4. The patellar ligament is struck with a tendon hammer, just below the patella. This stretches the quadriceps muscle. The alpha motor neurons carry efferent signals resulting in the contraction of the quadriceps muscle. Exaggerated reflex is seen in upper motor neuron lesion, hyperthyroidism, and anxiety. Decreased or absent reflex is known as the Westphal’s sign and may occur in lower motor neuron lesion and during sleep.
The ankle jerk, also known as the Achilles reflex, is performed by striking the Achilles tendonwhile keeping the foot dorsiflexed. The jerking of the foot towards the plantar surface indicates a positive reflex. This reflex occurs by S1 and S2 segments of the spinal cord. The absence of the reflex indicates hypothyroidism most commonly or disc herniation. A reduced ankle jerk reflex indicates peripheral neuropathy.
Comentários
Enviar um comentário